Developing and Deploying a Use-Inspired Metapopulation Modeling Framework for Detailed Tracking of Stratified Health Outcomes
1Decision and Infrastructure Sciences Division, Argonne National Laboratory, Lemont, IL, USA
2Chicago Department of Public Health, Chicago, IL, USA
Proceedings of the 2025 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC), IEEE, 2025
Abstract
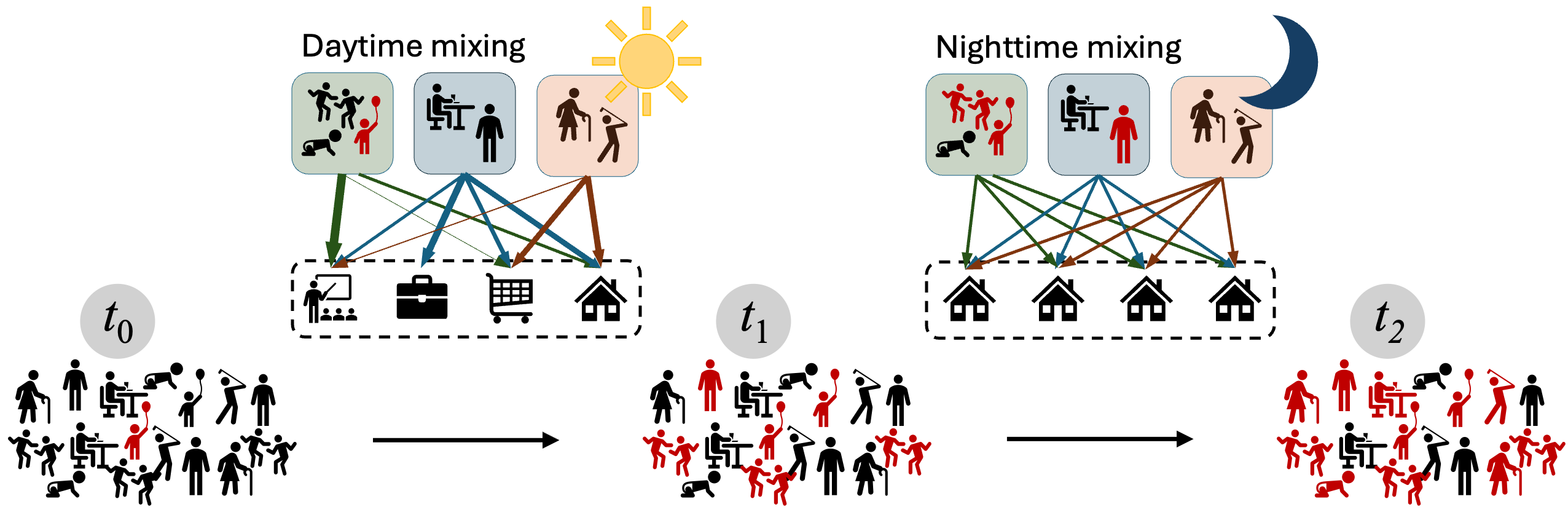
Public health teams often need granular and timely epidemiological insights without the heavy computational overhead of full agent-based simulation. This paper presents MetaRVM, an open-source R package for metapopulation modeling that supports flexible stratification by geography, demographics, and other user-defined subpopulations.
The framework was co-developed with the Chicago Department of Public Health to support operational decision-making. MetaRVM uses structured mixing across subpopulations and an extended SEIR-style disease progression model, enabling richer heterogeneity than homogeneous compartment models while remaining practical for routine use.
The paper demonstrates the framework on influenza in Chicago, including age-stratified outcome tracking and Bayesian optimization based calibration for efficient parameter estimation.
Key Contributions
Use-Inspired Framework
Introduces MetaRVM as a co-created framework designed with a public health partner for practical deployment, usability, and interpretability.
Stratified Metapopulation Dynamics
Models disease spread across interacting subpopulations using mixing matrices, bridging simple homogeneous models and computationally expensive agent-based models.
Calibration for Rapid Operations
Integrates an efficient Bayesian optimization based calibration workflow to support faster model tuning for real-world surveillance and planning timelines.
Applied Chicago Influenza Use Case
Demonstrates detailed age-stratified tracking of influenza dynamics and outcomes in Chicago, illustrating the framework's decision-support value for local health agencies.
Citation
BibTeX
@inproceedings{fadikar2025metarvm,
title={Developing and Deploying a Use-Inspired Metapopulation Modeling Framework for Detailed Tracking of Stratified Health Outcomes},
author={Fadikar, Arindam and Stevens, Abby and Rimer, Sara and Martinez-Moyano, Ignacio and Collier, Nicholson and Mabil, Chol and Jorgensen, Emile and Ruestow, Peter and McSorley, V. Eloesa and Ozik, Jonathan and Macal, Charles},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 2025 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC)},
year={2025},
organization={IEEE},
doi={10.1109/WSC68292.2025.11338996}
}Related Publications
- Adaptive Grid-Based Thompson Sampling for Efficient Trajectory Discovery - Related methodology paper
- IEEE Xplore record - Publisher page and metadata