Projects
A selection of projects that resulted in publications.
Machine learning synthetic spectra for probabilistic redshift estimation: SYTH-Z
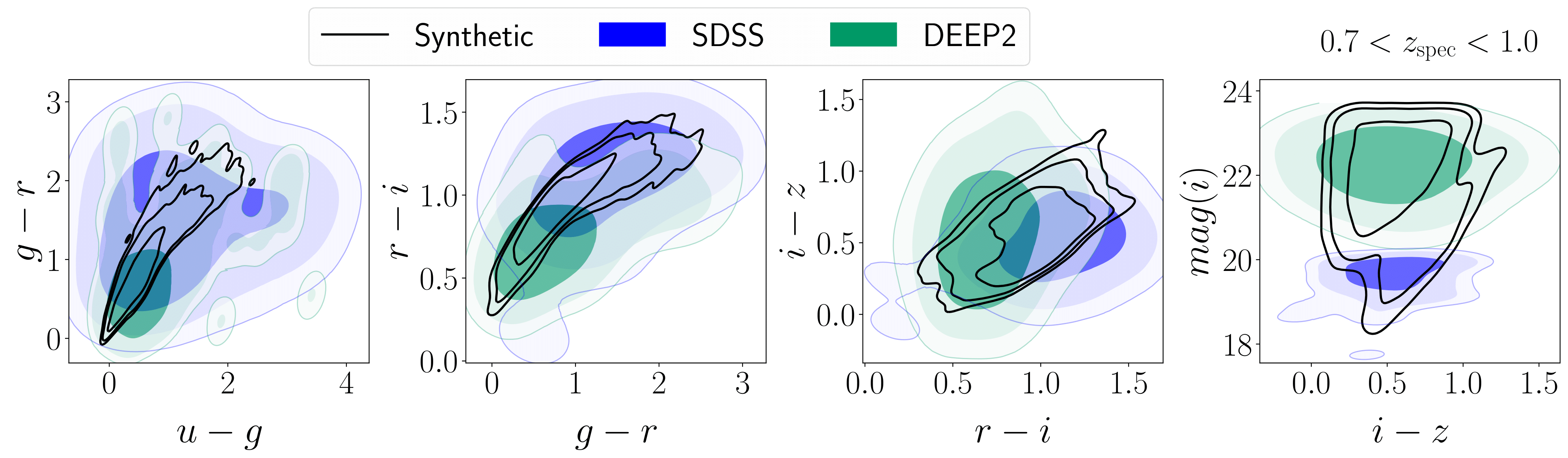
Photometric redshift estimation algorithms are often based on representative data from observational campaigns. Data-driven methods of this type are subject to a number of potential deficiencies, such as sample bias and incompleteness. Motivated by these considerations, we propose using physically motivated synthetic spectral energy distributions in redshift estimation.
Scalable Statistical Inference of Photometric Redshift via Data Subsampling
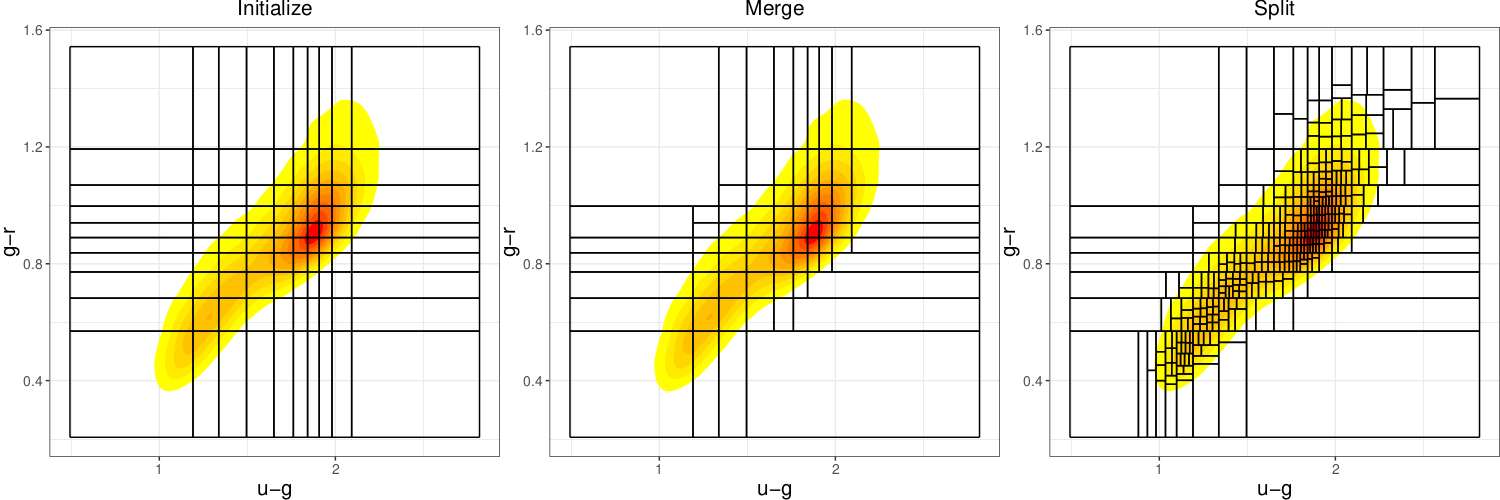
We develop a data-driven statistical modeling framework that combines the uncertainties from an ensemble of statistical models learned on smaller subsets of data carefully chosen to account for imbalances in the input space.
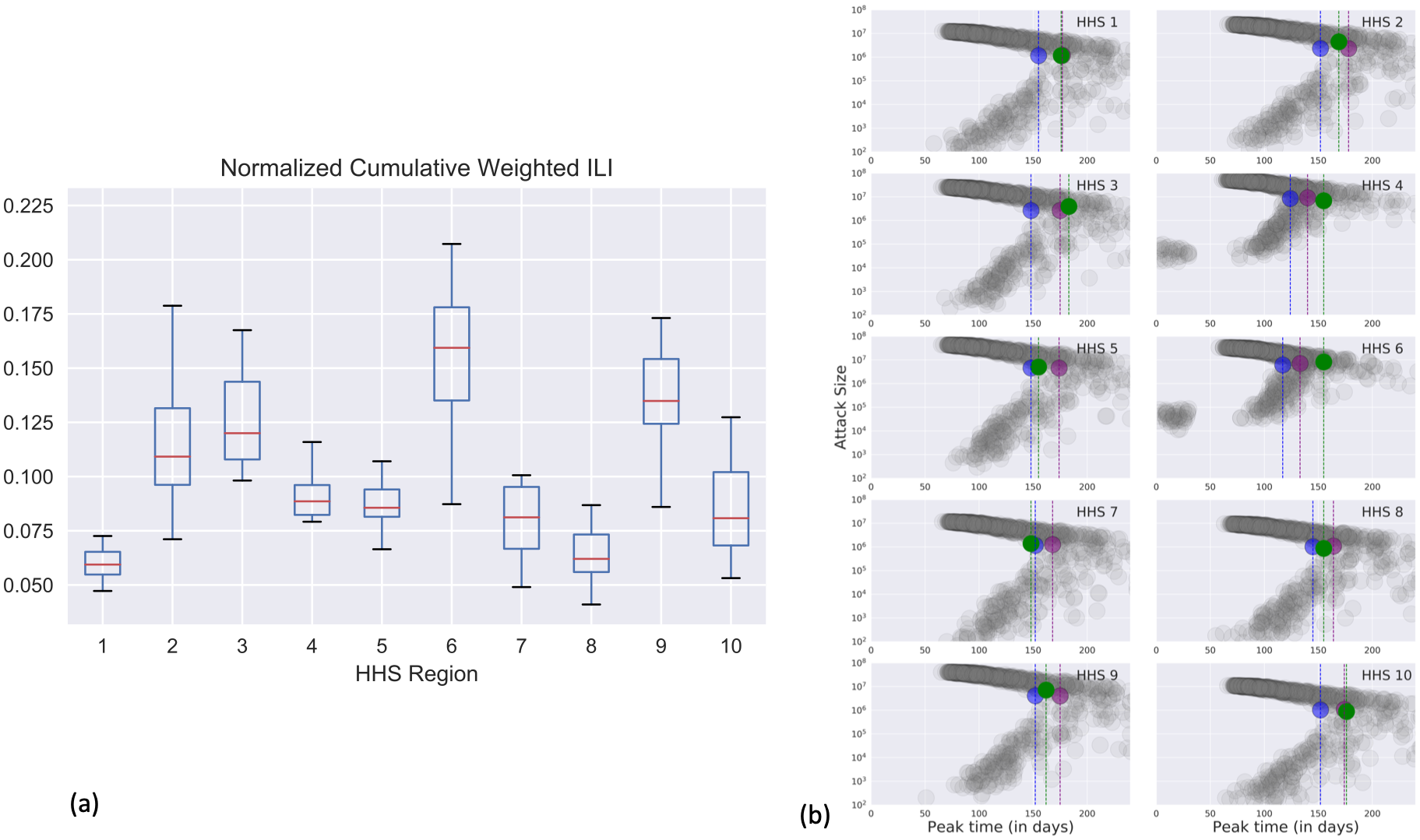
Forecasting influenza activity using machine-learned mobility map
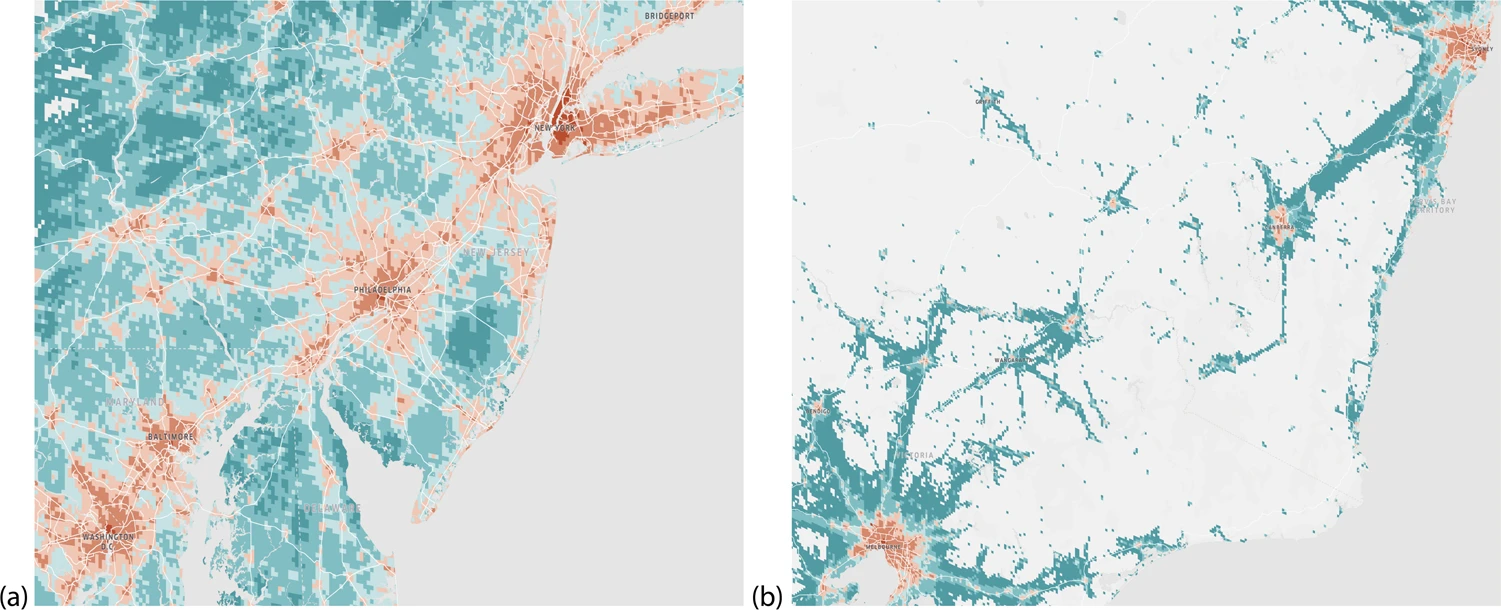
In this work, we focus on a machine-learned anonymized mobility map (AMM) aggregated over hundreds of millions of smartphones and evaluate its utility in forecasting epidemics. We factor AMM into a metapopulation model to retrospectively forecast influenza in the USA and Australia
Stochastic agent-based model calibration for Ebola
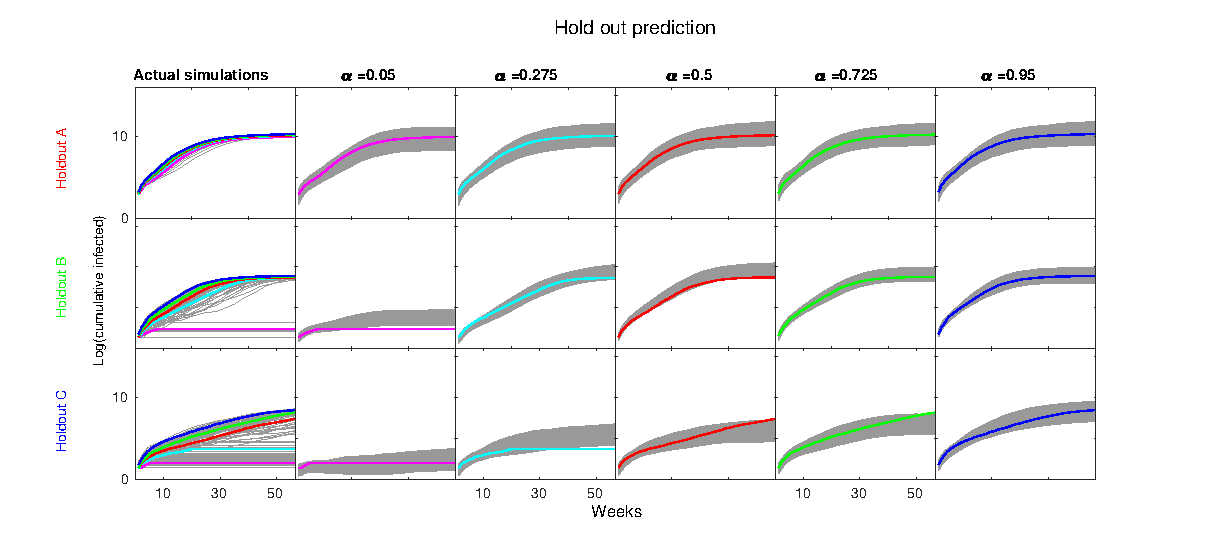
We develop a strategy to emulate and calibrate a stochastic agent-based model based on quantile kriging inside a Bayesian framework, where the agent-based model simulates an Ebola epidemic in West Africa.
Optimizing spatial allocation of seasonal influenza vaccine under temporal constraints
Annual vaccination campaigns continue to be one of the prime measures which help alleviate the burden of seasonal influenza. Due to production and logistic constraints, there is a need for prioritization policies associated with vaccine deployment. While there is general consensus on age-based or risk-based prioritization, spatial optimization of vaccine allocation has not yet been explored in sufficient detail. In order to do this, we develop a mechanistic model of influenza spread across the United States, and propose a greedy mechanism for spatial optimization. We test the methodology on different realistic scenarios with temporal constraints on vaccine production.
